Welcome to the world of production possibilities curve practice problems worksheet answers, where you will delve into the intricacies of economic decision-making. This comprehensive guide provides a thorough understanding of the production possibilities curve (PPC), its applications, and the trade-offs involved in resource allocation.
Through a series of practice problems and solutions, you will gain practical insights into the challenges and opportunities faced by economies as they strive to maximize production.
The production possibilities curve serves as a graphical representation of the various combinations of goods and services an economy can produce with its available resources and technology. By analyzing the PPC, economists can assess the opportunity costs of production, the impact of technological advancements, and the implications of international trade.
Understanding the PPC is crucial for policymakers and business leaders alike, as it helps them make informed decisions that drive economic growth and prosperity.
1. Definition and Explanation of Production Possibilities Curve
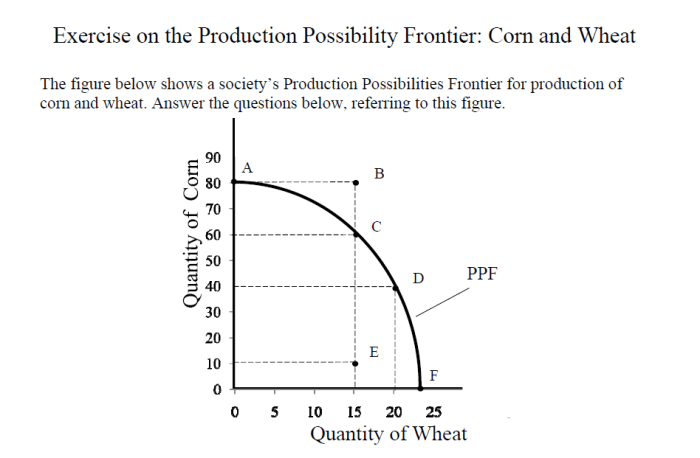
A production possibilities curve (PPC) is a graphical representation of the maximum possible combinations of two goods that an economy can produce with its given resources and technology. It shows the trade-offs that an economy faces in producing different goods.
PPCs are based on the following assumptions:
- The economy has fixed resources (labor, capital, land, and technology).
- The economy is producing efficiently, meaning it is using its resources in the most productive way possible.
- The economy is producing two goods.
PPCs can be used to illustrate the opportunity cost of producing one good over another. The opportunity cost is the amount of the other good that must be given up in order to produce one more unit of the first good.
PPCs can also be used to analyze the impact of economic growth. Economic growth shifts the PPC outward, allowing the economy to produce more of both goods.
2. Shifting Production Possibilities Curve
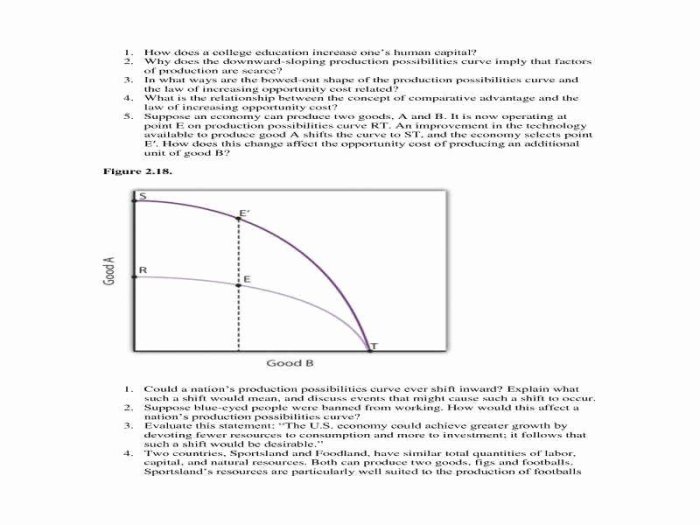
The PPC can shift outward or inward due to various factors.
Outward Shifts:
- Technological advancements
- Increased resource availability
- Improved labor productivity
Inward Shifts:, Production possibilities curve practice problems worksheet answers
- Natural disasters
- War or conflict
- Depletion of resources
3. Opportunity Cost and Trade-Offs
The opportunity cost of producing one good over another is the amount of the other good that must be given up in order to produce one more unit of the first good.
The trade-offs involved in choosing different points on the PPC are determined by the slope of the curve. A steeper slope indicates a higher opportunity cost, while a flatter slope indicates a lower opportunity cost.
Economic growth reduces the opportunity cost of producing goods. This is because economic growth shifts the PPC outward, allowing the economy to produce more of both goods with the same resources.
4. Applications of Production Possibilities Curve: Production Possibilities Curve Practice Problems Worksheet Answers

PPCs can be used to analyze the economic performance of countries, make informed policy decisions, and understand the implications of international trade.
For example, a country with a PPC that is shifted outward is experiencing economic growth. A country with a PPC that is shifted inward is experiencing economic decline.
PPCs can also be used to analyze the impact of different policies on the economy. For example, a policy that increases the availability of resources will shift the PPC outward, while a policy that reduces the availability of resources will shift the PPC inward.
5. Practice Problems and Solutions
Problem 1: An economy can produce either 100 units of good A or 50 units of good B. If the economy is currently producing 50 units of good A, what is the opportunity cost of producing one more unit of good A?
Solution: The opportunity cost of producing one more unit of good A is 1/2 unit of good B.
Problem 2: An economy is experiencing economic growth. As a result, the PPC shifts outward. What is the impact of this shift on the opportunity cost of producing goods?
Solution: The opportunity cost of producing goods decreases as a result of the outward shift in the PPC.
Questions Often Asked
What is the production possibilities curve?
The production possibilities curve is a graphical representation of the various combinations of goods and services an economy can produce with its available resources and technology.
What is opportunity cost?
Opportunity cost refers to the value of the next best alternative that is given up when a choice is made. In the context of the PPC, it represents the amount of one good that must be sacrificed to produce more of another.
How does technological advancement affect the PPC?
Technological advancement can shift the PPC outward, allowing an economy to produce more of both goods without sacrificing either.