Match each pathogen with its mode of transmission – Delving into the intricate world of pathogens, we embark on a journey to uncover the diverse modes of transmission employed by these microscopic entities. From the stealthy bacteria to the enigmatic viruses, the cunning fungi to the insidious parasites, each pathogen possesses unique strategies for spreading its infectious reach.
As we delve deeper into the topic, we will meticulously examine the various transmission routes, exploring the mechanisms by which pathogens exploit our bodies and the environment to perpetuate their existence. By unraveling these intricate processes, we gain invaluable insights into the epidemiology and prevention of infectious diseases, safeguarding human health and well-being.
Bacterial Pathogens: Match Each Pathogen With Its Mode Of Transmission
Bacterial pathogens can be transmitted through various modes, including:
- Contact transmission:Direct contact with an infected person or contaminated surfaces, e.g., Staphylococcus aureus (skin infections)
- Droplet transmission:Inhalation of respiratory droplets containing bacteria, e.g., Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumonia)
- Airborne transmission:Inhalation of bacteria suspended in the air, e.g., Mycobacterium tuberculosis (tuberculosis)
- Foodborne transmission:Consumption of contaminated food, e.g., Salmonella enterica (food poisoning)
- Waterborne transmission:Ingestion of contaminated water, e.g., Vibrio cholerae (cholera)
Viral Pathogens

Viral pathogens can be transmitted through:
- Contact transmission:Direct contact with an infected person or contaminated surfaces, e.g., Herpes simplex virus (cold sores)
- Droplet transmission:Inhalation of respiratory droplets containing viruses, e.g., Influenza virus (flu)
- Airborne transmission:Inhalation of viruses suspended in the air, e.g., Measles virus (measles)
- Bloodborne transmission:Contact with infected blood or body fluids, e.g., Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
- Vector-borne transmission:Transmitted by insects or animals, e.g., Dengue virus (dengue fever)
Fungal Pathogens
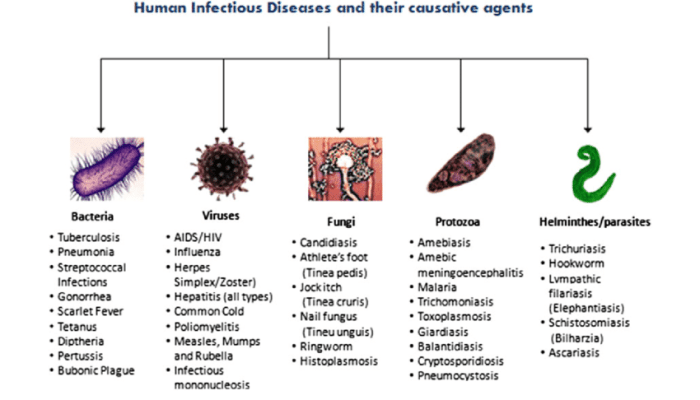
Fungal pathogens are primarily transmitted through:
- Contact transmission:Direct contact with an infected person or contaminated surfaces, e.g., Candida albicans (yeast infections)
- Airborne transmission:Inhalation of fungal spores, e.g., Aspergillus fumigatus (aspergillosis)
- Soilborne transmission:Contact with contaminated soil, e.g., Histoplasma capsulatum (histoplasmosis)
Parasitic Pathogens
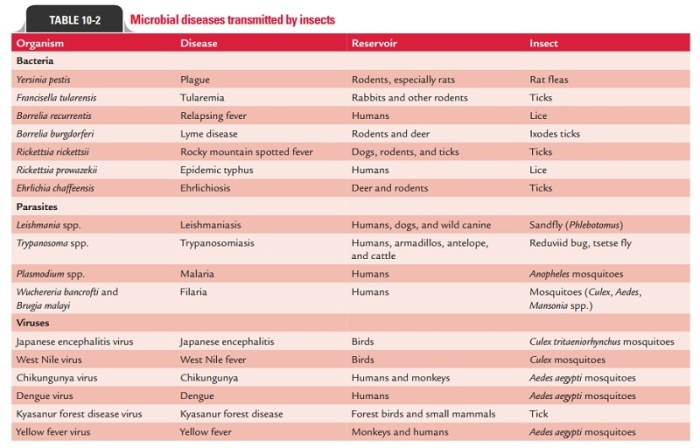
Parasitic pathogens can be transmitted in various ways, including:
- Contact transmission:Direct contact with an infected person or contaminated surfaces, e.g., Enterobius vermicularis (pinworms)
- Ingestion:Consumption of contaminated food or water, e.g., Toxoplasma gondii (toxoplasmosis)
- Vector-borne transmission:Transmitted by insects or animals, e.g., Plasmodium falciparum (malaria)
Mode of Transmission Comparison
| Pathogen Type | Transmission Route | Specific Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Bacteria | Contact | Staphylococcus aureus |
| Bacteria | Droplet | Streptococcus pneumoniae |
| Bacteria | Airborne | Mycobacterium tuberculosis |
| Virus | Contact | Herpes simplex virus |
| Virus | Droplet | Influenza virus |
| Virus | Airborne | Measles virus |
| Fungus | Contact | Candida albicans |
| Fungus | Airborne | Aspergillus fumigatus |
| Parasite | Contact | Enterobius vermicularis |
| Parasite | Ingestion | Toxoplasma gondii |
| Parasite | Vector-borne | Plasmodium falciparum |
Essential Questionnaire
What are the most common modes of transmission for bacterial pathogens?
Bacterial pathogens can be transmitted through various routes, including direct contact with infected individuals or contaminated surfaces, ingestion of contaminated food or water, and inhalation of airborne droplets.
How do viral pathogens differ in their transmission mechanisms compared to bacterial pathogens?
Viral pathogens often spread through respiratory droplets or aerosols, but they can also be transmitted through contact with infected bodily fluids, contaminated surfaces, or insect vectors.
What are the unique transmission characteristics of fungal pathogens?
Fungal pathogens can be transmitted through inhalation of spores, direct contact with infected individuals or surfaces, or through contaminated soil or water.
How do parasitic pathogens exploit different hosts to complete their life cycles?
Parasitic pathogens exhibit complex life cycles, often involving multiple hosts. They can be transmitted through direct contact, ingestion of contaminated food or water, or through insect vectors.