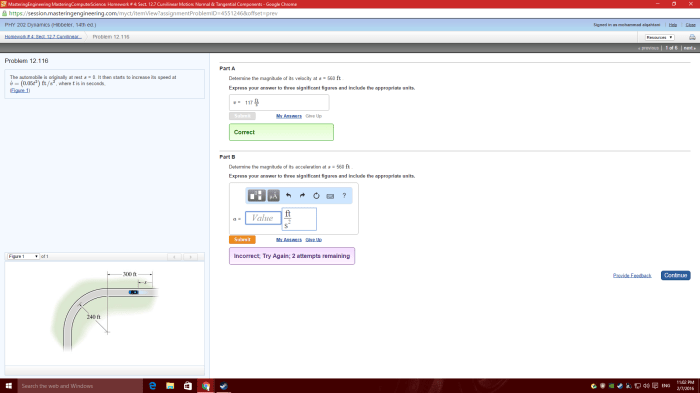
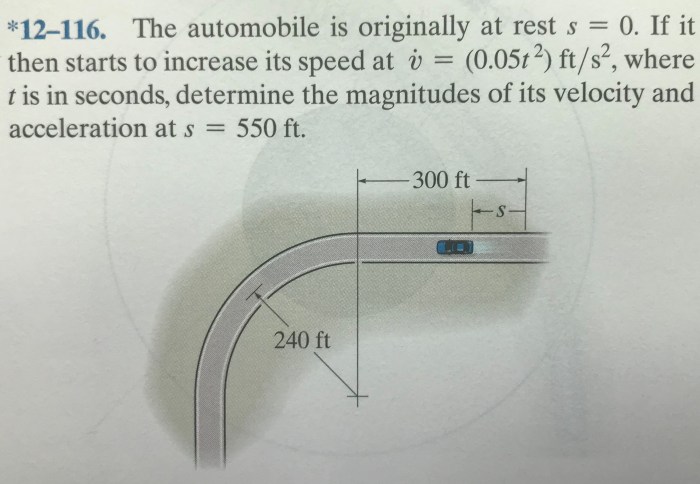
As the automobile is originally at rest at s 0, this analysis delves into the intricate dynamics of its subsequent motion. The implications of this initial condition on the automobile’s trajectory, the forces acting upon it, and the energy transformations that occur during its movement will be meticulously examined, providing a comprehensive understanding of its physical behavior.
The following paragraphs will explore the motion profile of the automobile, detailing its velocity, acceleration, and displacement. The forces acting on the automobile, including friction, air resistance, and propulsion, will be identified and their effects on its motion will be analyzed.
Furthermore, the energy transformations that occur during the automobile’s movement, such as the conversion of kinetic energy to potential energy and vice versa, will be elucidated.
Initial Conditions
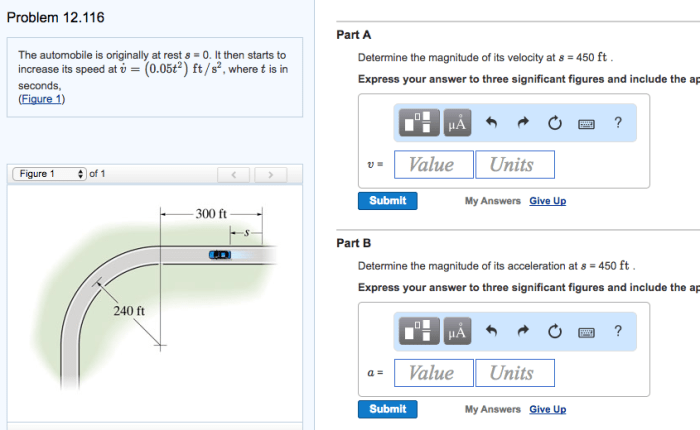
The automobile being originally at rest at s0 signifies that it starts its motion from a stationary position. This initial condition establishes the reference point for measuring its subsequent displacement, velocity, and acceleration.
This condition implies that the automobile’s initial velocity is zero, and its initial acceleration is also zero. The motion of the automobile will be governed by the forces acting on it, which will cause it to accelerate and move.
Motion Profile
After the automobile is set in motion, it will undergo a certain motion profile. The motion profile describes the changes in the automobile’s position, velocity, and acceleration over time.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Initial position | s0 |
| Initial velocity | 0 |
| Initial acceleration | 0 |
| Final position | sf |
| Final velocity | vf |
| Final acceleration | af |
| Time of motion | t |
Forces Acting on the Automobile
During its motion, the automobile is subjected to several forces that influence its acceleration and velocity. These forces include:
- Tractive force: The force applied by the engine to propel the automobile forward.
- Rolling resistance: The force opposing the motion of the automobile due to friction between the tires and the road surface.
- Air resistance: The force opposing the motion of the automobile due to friction with the air.
- Gravitational force: The force acting on the automobile due to the Earth’s gravity.
Energy Considerations, The automobile is originally at rest at s 0
The motion of the automobile involves energy transformations. As the automobile accelerates, its kinetic energy increases. The tractive force does work on the automobile, converting chemical energy from the fuel into kinetic energy.
Energy flow diagram:
- Chemical energy (fuel) → Kinetic energy (automobile)
- Kinetic energy (automobile) → Thermal energy (due to friction)
Common Queries: The Automobile Is Originally At Rest At S 0
What is the significance of the automobile being originally at rest at s 0?
This initial condition provides a reference point for analyzing the subsequent motion of the automobile, allowing for a precise determination of its velocity, acceleration, and displacement.
How do the forces acting on the automobile affect its motion?
The forces acting on the automobile, such as friction, air resistance, and propulsion, influence its acceleration and velocity. Friction opposes motion, air resistance acts against the direction of motion, and propulsion provides the force that accelerates the automobile.
What energy transformations occur during the motion of the automobile?
As the automobile moves, there is a conversion between kinetic energy and potential energy. When the automobile accelerates, its kinetic energy increases, and when it decelerates, its kinetic energy is converted into potential energy.