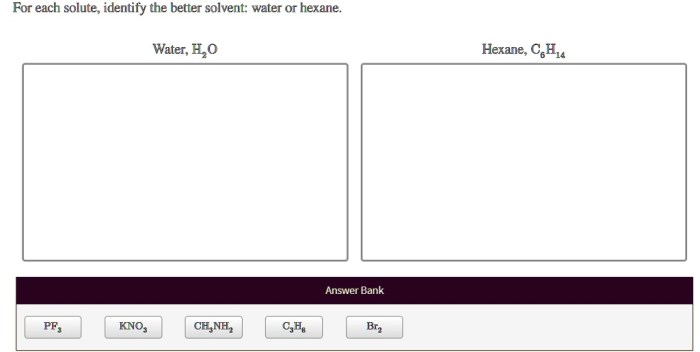
Select the more electronegative element in this pair. – Select the more electronegative element in this pair: a fundamental concept in chemistry that governs the formation and properties of chemical bonds. Electronegativity, a measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons, plays a crucial role in determining the polarity of bonds, molecular geometry, and reactivity.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of electronegativity, providing a step-by-step approach to selecting the more electronegative element in a pair. With real-world examples and practical applications, we explore the significance of electronegativity in shaping the chemical landscape.
Understanding Electronegativity

Electronegativity is a measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons towards itself in a chemical bond. It is a fundamental property of elements that plays a crucial role in determining their chemical behavior and the properties of the compounds they form.
Highly electronegative elements have a strong tendency to attract electrons, while less electronegative elements have a weaker attraction for electrons. Some of the most electronegative elements include fluorine, oxygen, nitrogen, and chlorine.
Electronegativity is influenced by several factors, including atomic size, nuclear charge, and electron configuration.
Selecting the More Electronegative Element: Select The More Electronegative Element In This Pair.

To select the more electronegative element in a pair, we can compare their electronegativity values. The element with the higher electronegativity value is more electronegative.
| Element | Electronegativity Value | Selection |
|---|---|---|
| Fluorine | 4.0 | More electronegative |
| Oxygen | 3.5 | Less electronegative |
The following flowchart illustrates the decision-making process:

Applications of Electronegativity

Electronegativity has numerous applications in chemistry. It helps us understand and predict:
- The type of chemical bond formed between atoms
- The polarity of molecules
- The reactivity of elements
For example, electronegativity can be used to predict the type of bond formed between two elements. If the electronegativity difference between the elements is large, an ionic bond is likely to form. If the electronegativity difference is small, a covalent bond is likely to form.
Limitations of Electronegativity

While electronegativity is a useful concept, it has some limitations:
- It is not always a reliable predictor of chemical behavior, especially in complex molecules.
- Electronegativity values can vary depending on the context, such as the bonding environment and the presence of other atoms.
Despite these limitations, electronegativity remains a valuable tool for understanding and predicting chemical behavior.
FAQ Summary
What is electronegativity?
Electronegativity is a measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons in a chemical bond.
Which element is more electronegative, chlorine or fluorine?
Fluorine is more electronegative than chlorine.
How does electronegativity affect chemical bonding?
Electronegativity influences the polarity of chemical bonds, with more electronegative elements attracting electrons towards themselves, creating a partial negative charge.