Shelter on the Asian steppes unfolds a captivating narrative of human ingenuity and adaptation. Across vast landscapes, from rolling grasslands to towering mountains, nomadic peoples and modern dwellers have crafted unique shelters that reflect their cultural heritage and the challenges of their environment.
From the traditional yurts of Central Asia to the modern apartments of urban centers, this exploration delves into the construction methods, materials, and cultural significance of shelters on the steppes, showcasing the resilience and creativity of those who call this vast region home.
Geographic Overview
The Asian steppes encompass a vast and diverse expanse of landscapes, stretching across the heart of Asia from the eastern shores of the Black Sea to the western borders of China. This vast region is characterized by its seemingly endless grasslands, punctuated by rugged mountain ranges and arid deserts.
The terrain of the steppes is as varied as its geography. The rolling grasslands, known as “steppes” in Russian, dominate the landscape, providing fertile grazing grounds for nomadic herders. However, the steppes are not without their challenges. Arid deserts, such as the Gobi Desert, present harsh conditions for life, while the towering peaks of mountain ranges, like the Altai Mountains, create formidable barriers to travel.
Climate
The climate of the steppes is continental, with extreme temperatures and limited rainfall. Summers can be scorching, with temperatures reaching up to 40 degrees Celsius (104 degrees Fahrenheit), while winters are bitterly cold, with temperatures plummeting below -30 degrees Celsius (-22 degrees Fahrenheit).
The lack of rainfall, combined with the strong winds that sweep across the steppes, creates a dry and arid environment.
The availability of shelter on the Asian steppes is greatly influenced by the climate. During the harsh winters, nomadic herders seek refuge in temporary shelters made from animal skins or felt, providing protection from the cold and wind. In contrast, during the hot summers, they often rely on portable tents or yurts, which offer shade and ventilation.
The Asian steppes, with their vast open spaces and extreme temperatures, demanded shelters that could withstand both the elements and nomadic lifestyles. Yurts, portable and durable structures, were often adorned with intricate patterns reflecting the fascial lines of the body, fascial lines being the interconnected web of connective tissues that shape our bodies.
This connection between shelter and the human form highlights the integral role of our environment in shaping our physicality and cultural expression.
Traditional Shelters

Nomadic peoples on the vast Asian steppes have developed ingenious shelters that provide protection from the harsh and unforgiving environment. These traditional dwellings, ranging from yurts to gers and tents, are portable and adaptable to the varied conditions encountered across the steppe.
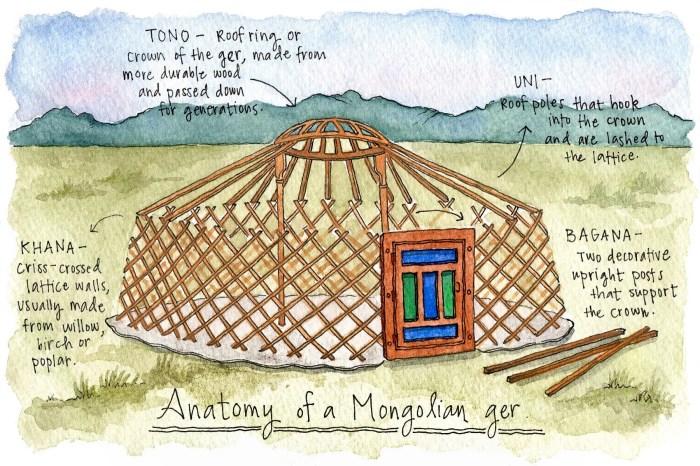
Yurts, also known as gers in Mongolia, are iconic circular structures constructed from a wooden frame covered with felt or animal skins. The domed shape ensures stability in strong winds, while the thick felt insulation provides warmth during cold nights and insulation against summer heat.
Construction Methods and Materials
Yurts are typically assembled by multiple people and can be erected or dismantled within a few hours. The wooden frame consists of a central roof ring, wall frames, and a door frame. The felt covering is cut into sections and sewn together, then stretched over the frame and secured with ropes.
Animal skins, such as sheepskin or goat hide, may be used to provide additional insulation and weather resistance.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Yurts offer several advantages. Their circular shape and flexible structure make them highly wind-resistant, and the felt insulation provides excellent thermal protection. They are also relatively easy to transport and can be packed away when the nomads move.
However, yurts can be heavy and require a significant amount of space to set up. Additionally, the felt covering can be susceptible to damage from rain or snow if not properly maintained.
Modern Shelters
Modern shelters used by people living on the Asian steppes have evolved to meet the changing needs and lifestyles of the region’s inhabitants. These shelters include houses, apartments, and mobile homes, each with its own advantages and disadvantages in the steppe environment.
Houses
Houses are the most common type of permanent shelter on the steppes. They are typically made of brick, wood, or concrete and feature a variety of designs, from traditional to modern. Houses provide ample space and comfort for families, with multiple rooms, kitchens, bathrooms, and often outdoor areas.
One advantage of houses is their durability and ability to withstand the harsh steppe climate. Brick and concrete houses are particularly resilient to strong winds and extreme temperatures. However, houses can be expensive to build and maintain, and they are not easily transportable if necessary.
Apartments
Apartments are another popular option for housing on the steppes. They are typically located in urban areas and offer a more affordable and convenient lifestyle than houses. Apartments are often smaller than houses, but they provide all the essential amenities, including kitchens, bathrooms, and living areas.
One advantage of apartments is their affordability and ease of maintenance. They are typically cheaper to rent or buy than houses, and they require less upkeep. However, apartments can be less spacious than houses and may not offer the same level of privacy.
Mobile Homes
Mobile homes are a unique type of shelter that is becoming increasingly popular on the steppes. They are typically built on a trailer frame and can be easily transported from one location to another. Mobile homes offer a more flexible and affordable housing option than houses or apartments.
One advantage of mobile homes is their mobility. They can be moved to different locations as needed, which is particularly useful for people who work in remote areas or who travel frequently. However, mobile homes can be less durable than houses and apartments, and they may not be suitable for all climates.
Shelter Adaptations

Shelters on the Asian steppes have evolved over centuries to withstand the region’s extreme weather conditions. These adaptations include insulation, heating, and ventilation systems that provide comfort and protection from the harsh environment.
The adaptations vary depending on the specific steppe environment, but some common features include:
Insulation, Shelter on the asian steppes
- Thick walls made of materials such as mud, stone, or animal skins
- Insulating layers of straw, hay, or felt
- Double-layered roofs with an air gap between them
Heating
- Fireplaces or stoves
- Underfloor heating systems
- Passive solar heating through large windows facing south
Ventilation
- Openings in the roof or walls
- Adjustable vents to control airflow
- Chimneys to remove smoke and fumes
These adaptations work together to create shelters that are both comfortable and protective in the challenging climate of the Asian steppes.
Cultural and Social Aspects of Shelter: Shelter On The Asian Steppes
On the vast Asian steppes, shelter has profound cultural and social significance. It goes beyond mere protection from the elements; it shapes identities, defines relationships, and serves as a canvas for communal rituals.
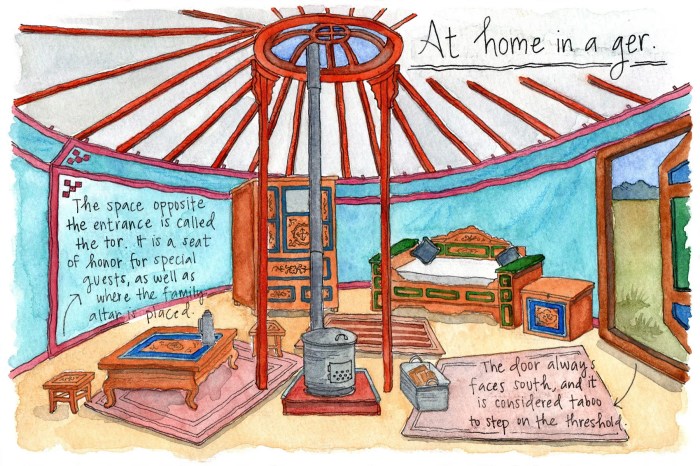
Yurts, the traditional portable dwellings, are more than just homes. They are symbols of status and hospitality. The size and ornamentation of a yurt reflect the wealth and prestige of the family that occupies it. The interior layout, with its designated spaces for different family members and guests, reinforces traditional social hierarchies.
Shelter in Traditional Ceremonies and Rituals
Shelter plays a central role in many traditional ceremonies and rituals on the steppes. During weddings, the yurt becomes a sacred space where the couple is united. In funerals, the yurt serves as a place for mourning and remembrance. And during festivals, yurts are adorned with colorful decorations and become gathering places for the community.
Questions Often Asked
What is the most common type of traditional shelter on the Asian steppes?
The yurt, a portable, circular dwelling made of felt and wood, is the most prevalent traditional shelter on the Asian steppes.
How do modern shelters on the steppes differ from traditional ones?
Modern shelters are typically constructed using permanent materials like brick, concrete, and metal, and feature amenities such as electricity, plumbing, and heating systems.
What adaptations are made to shelters on the steppes to cope with extreme weather conditions?
Shelters on the steppes are often insulated with materials like wool or felt to provide warmth during cold winters. Ventilation systems are also crucial for regulating temperature and preventing condensation.
